Click here to get this post in PDF
What Is Allocation Unit Size?
As we all know, hard drive space is composed of sectors, which are the smallest data reading and writing units at the disk level. As for allocation unit size, it is also called “cluster”, which is the smallest data reading and writing unit at the file system level.
When you want to write data into a hard disk, the process should be as follows:
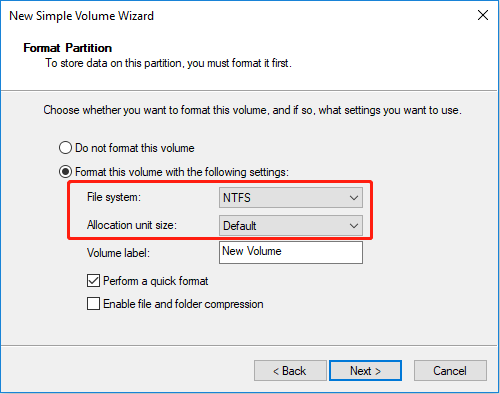
1. Create a partition in the hard drive. In this step, the OS will allow you to determine the file system of the partition (NTFS, FAT32, etc.) and the allocation unit size (cluster size) of the partition.
2. After the partition is created, you can then write data to the hard disk (for example, copy files into the partition). In this step, files are first stored in logical sectors in the unit of clusters, and then they are stored into physical sectors of the hard disk.
Source: www.partitionwizard.com
The Relationship Among Physical Sectors, Logical Sectors, and Clusters
After reading the above data storage process, you may want to know about the relationship among physical sectors, logical sectors, and clusters. Please read the following contents to get the answer.
Physical Sector and Logical Sector
A disk’s space is composed of many sectors (disk space = sector size * the number of sectors). However, the physical sector cannot be directly accessed by OS. The OS can only access logical sectors.
Physical sector size and logical sector size are determined by the hard disk manufacture industry. In most cases, the hard disk sector is as follows:
| Format | Logical Sector Size (bytes) | Physical Sector Size (bytes) |
| 512n | 512 | 512 |
| 512e | 512 | 4096 |
| 4Kn | 4096 | 4096 |
512n hard disks are the old type of disks, which have 512 bytes physical sectors. To make better use of hard drive space, starting from 2010, hard disk companies have gradually migrated sectors from the traditional size of 512 bytes to 4096 bytes. Nowadays, almost all hard drives on the market are 4 K hard drives (512e or 4Kn).
The transition from 512n to 4Kn is not an overnight process. During this transition period, software compatibility problems will occur. For example, old host computer hardware and software components adopting 521-byte-sector disks cannot run well on 4Kn hard drives. To solve this issue, 512e hard disks come out.
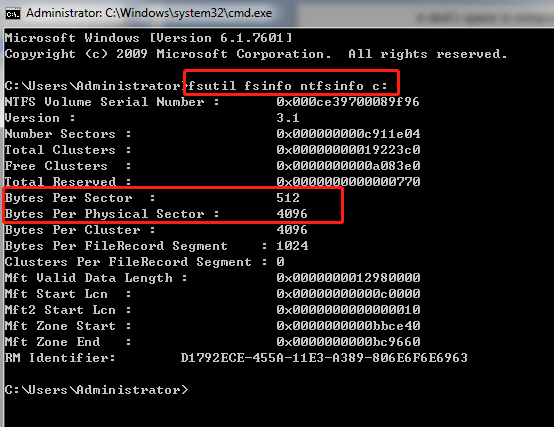
To know what hard drive you are using, you can open cmd and use the command “fsutil fsinfo ntfsinfo c:“. This command will tell you bytes per sector, bytes per physical sector, and bytes per cluster.
Source: www.partitionwizard.com
As you can see, a physical sector can contain one or more logical sectors.
Note: When the physical sector size and the logical sector size are not the same, the 4K alignment issue will happen.
Sector and Cluster
The logical sectors in a hard disk are too many to be addressed by the file system. Therefore, the file system combines adjacent sectors to form an allocation unit, and then it can manage data in the unit of clusters to efficiently utilize resources. So, a cluster can also contain one or more logical sectors.
In general, a cluster is composed of 2n logical sectors (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, etc.). The capacity of a partition is equal to cluster size * the number of clusters.
The Importance of the Allocation Unit Size
The allocation unit size will affect disk space utilization and disk performance. The bigger the cluster, the better the disk performance. The smaller the cluster, the better the disk space utilization. The principle is as follows (taking 5 KB data as an example):
- If you plan to store 5 KB data into a partition with clusters of 512 bytes, the data will use 10 clusters and no space is wasted.
- If you plan to store 5 KB data into a partition with clusters of 4KB, the data will use 2 clusters (8 KB space). Because a cluster can only be occupied by one file, 3 KB space (8KB minus 5KB) will be wasted.
On the other hand, if you use fewer clusters to save data, the OS will look for the data more easily, reaching faster data access speed.
What Allocation Unit Size Should I Use for FAT32?
What allocation unit size should I use for FAT32? To get a proper FAT32 allocation unit size, you should consider the following factors:
1. The balance between disk performance and disk space utilization.
2. Partition capacity. Cluster size will affect the capacity of the partition. The larger the cluster, the larger the partition capacity.
How to change FAT32 allocation unit size? Can I change the cluster size without formatting? Is there any recommended FAT32 allocation unit size? Please refer to the original post to get the answers.
You may also like: How Do I Know If My Laptop Is Upgradeable?